ORCA v1
$ 5 889

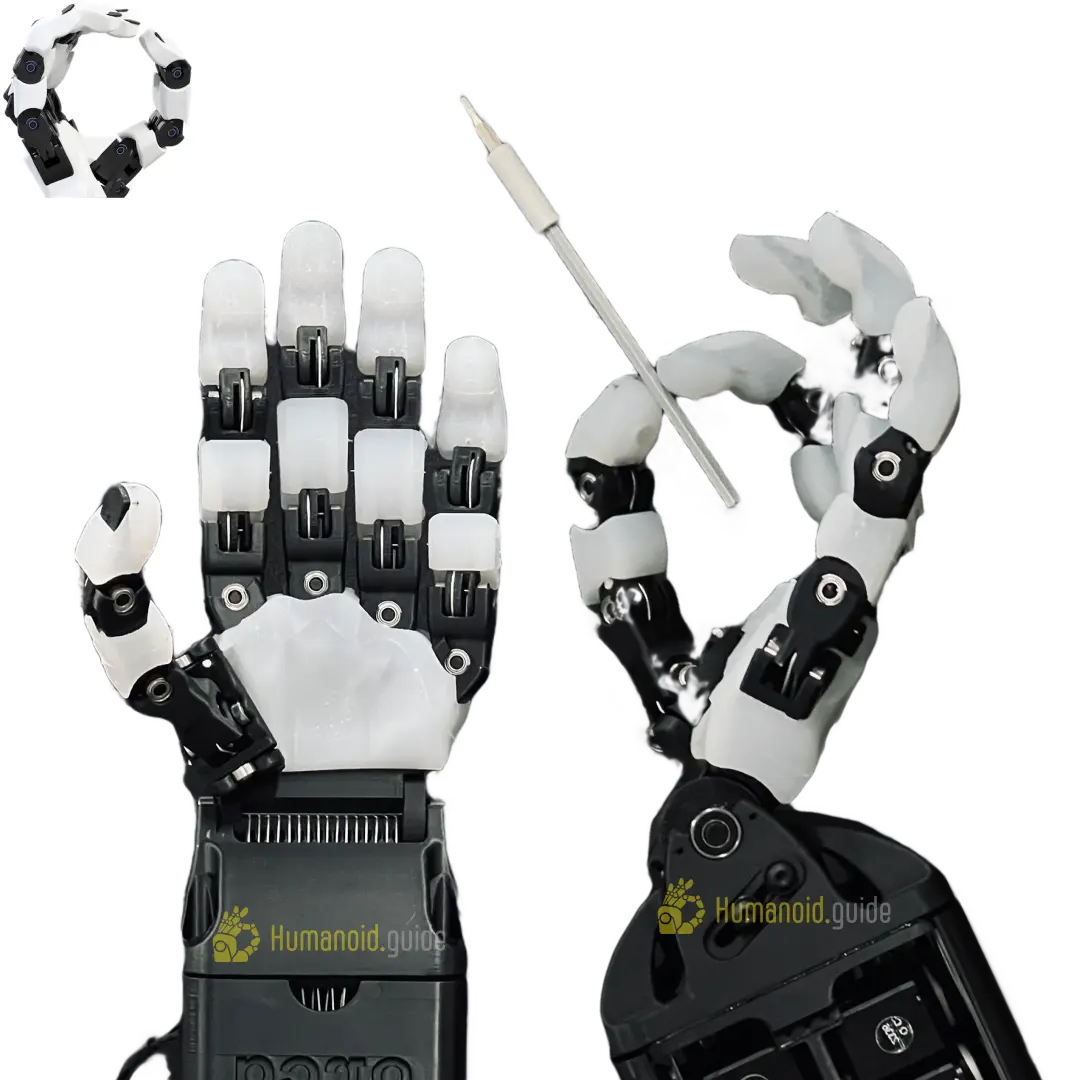
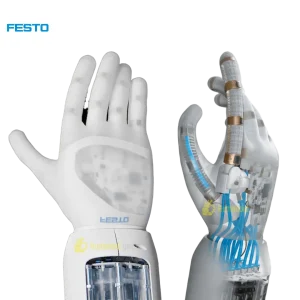
The ORCA v1 is an open-source, human-like robotic hand that blends realistic anatomy with accessible hardware. It offers 17 active degrees of freedom and a tendon-driven structure, enabling versatile, dexterous manipulation suitable for research, education, or creative robotics projects.
Available on backorder
Specifications and details:
| Strength [kg] | N/A |
|---|---|
| Weight [kg] | ~ 1.3 |
| Size | anthropomorphic, roughly human-hand sized |
| Number of fingers | 5 (thumb + four fingers) — human-like hand configuration |
| Degrees of freedom, hands | 17 active DoF (16 in fingers, 1 in wrist) |
| Motor tech | Uses Dynamixel servos (e.g. XC330-T228T and XC430-T240BB-T) |
| Main structural material | 3D-printed parts (e.g. PLA or similar), covered with silicone cast skin for compliance and tactile grip |
| Manufacturer | ORCA Hand / Soft Robotics Lab (ETH Zürich) |
| Nationality | Switzerland |
| Website | https://www.orcahand.com |
Description
The ORCA v1 hand aims to give robots a human-like grasp and feel. It closely mirrors the shape and joint layout of a human hand, including an opposable thumb and articulated fingers — which lets it hold and manipulate everyday objects naturally. Because of its realistic proportions and joint configuration, it works well for teleoperation, imitation learning, or any project that builds on human-hand movements.
2026 Humanoid Robot Market Report
Interested in the ORCA v1? Download 160 pages of exclusive insight from global robotics experts – uncover funding trends, technology challenges, leading manufacturers, supply chain shifts, and surveys and forecasts on future humanoid applications.
Featuring insights from
Rob Knight
Open source,
humanoid expert

2026 Humanoid Robot Market Report
160 pages of exclusive insight from global robotics experts – uncover funding trends, technology challenges, leading manufacturers, supply chain shifts, and surveys and forecasts on future humanoid applications.
What makes ORCA v1 especially appealing is its accessibility. The creators built it to be affordable and easy to reproduce: many of its structural parts come from 3D-printed soft-skin designs and standard off-the-shelf motors. As a result, it became much simpler for labs, students, or hobbyists to build and experiment with a high-quality robotic hand.
Download the Humanoid Robot Market Report here