Chinese Humanoid Robot Makers Target US Market After CES 2026
Chinese humanoid robot developers are accelerating plans to enter the US market, following a strong showing at CES 2026 where more than 20 companies from China presented full scale humanoid systems. The displays highlighted rapid progress in locomotion, manipulation, and system integration, positioning Chinese vendors as emerging competitors to US based humanoid robotics firms.
2026 Humanoid Robot Market Report
160 pages of exclusive insight from global robotics experts – uncover funding trends, technology challenges, leading manufacturers, supply chain shifts, and surveys and forecasts on future humanoid applications.

Featuring insights from
Aaron Saunders, Former CTO of
Boston Dynamics,
now Google DeepMind

2026 Humanoid Robot Market Report
160 pages of exclusive insight from global robotics experts – uncover funding trends, technology challenges, leading manufacturers, supply chain shifts, and surveys and forecasts on future humanoid applications.
CES 2026 signals broader market ambitions
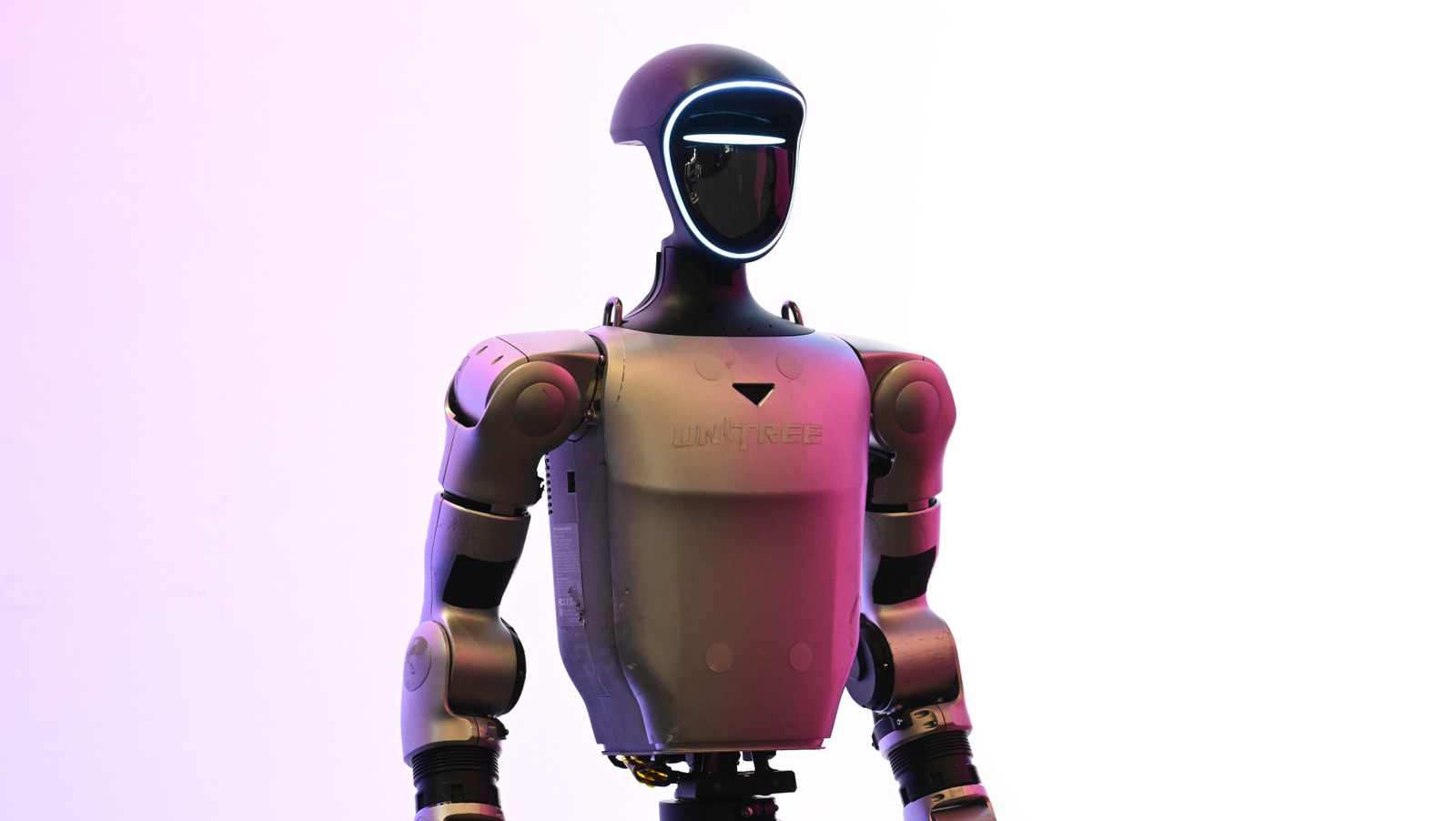
According to reporting from BGR, companies such as Unitree Robotics and AgiBot demonstrated humanoid platforms capable of stable bipedal walking, object handling, and basic task execution. Several of these systems were shown operating untethered, with integrated perception and onboard compute rather than relying on staged demos.
Unitree, already known in the US for its quadruped robots, used CES to emphasize its humanoid roadmap and manufacturing scale. AgiBot and other startups highlighted designs aimed at logistics, inspection, and service scenarios rather than research only prototypes.
Cost structure and iteration speed
A key differentiator highlighted by observers is cost. Chinese humanoid platforms are being positioned at significantly lower price points than comparable Western systems, driven by domestic supply chains and vertically integrated manufacturing. This pricing strategy could appeal to early enterprise adopters seeking to pilot humanoid robots without committing to high capital expenditure.
Equally important is iteration speed. Several vendors demonstrated hardware revisions and software updates developed within months, reflecting a fast development cycle that mirrors trends seen previously in drones and industrial robotics.
Technical maturity and limitations
Despite visible progress, the robots shown remain constrained in autonomy and reliability. Most demonstrations focused on scripted tasks, supervised operation, or narrow use cases. Battery life, payload capacity, and long term durability were not fully addressed in public demonstrations.
However, incremental improvements in balance control, hand dexterity, and vision based manipulation suggest a steady move toward practical deployments in controlled environments.
Implications for the US humanoid market
For US based developers and integrators, the entry of Chinese humanoid robots introduces new competitive pressure on pricing and time to market. At the same time, regulatory scrutiny, trade restrictions, and data security considerations are likely to shape how quickly these systems can be deployed at scale in the US.
The CES 2026 presence indicates that Chinese humanoid robot makers are no longer focused solely on domestic pilots. The next phase will depend on whether these platforms can transition from demonstrations to sustained operation in real world industrial and service settings.